Watch-paper of Sam Toulmin, The Strand, London

Watch-paper of Rob Fleetwood, London

Thos. Field Watch Maker
Aylesbury
Wedding & Mourning
Rings made Likewise
most Money given for
Second Hand Plate
Watches &c
[note: the above 3 watchpapers have equation tables]

George Prior Clock and Watchmaker
in Prescot St Goodman's Field, London

Un-cut watch-paper/trade-card of
Richard Whiteaves, Clock & Watch Maker
Fleet Street, London [1801]

Watch-paper of William Loudan,
Blackfriars, London (maybe 1825-1840)

Igglesden Watch Maker,
Silversmith & Jeweller,
High Street Chatham
[garter-belt border bearing inscription]

Green cut edged with yellow centre watch-paper,
stylised sunflower, with smiley face, in outer case. (~1732-1770)

Richardson Watch & Clock Maker, Brampton
To Make a Watch go Slower
turn the Regulator the same way you Wind up,
Faster the contrary

Thos. Brown
Clock & Watch Maker
Birmingham (1796)

John Jarvis
Watch & Clock Maker
Whitchurch
All kinds of Clocks Watches
Musical Boxes Plate Jewellery &c
cleaned & repaired
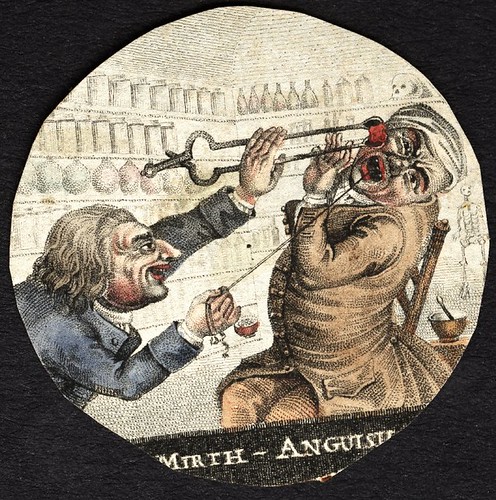

Mirth - Anguish
(coloured print of dentist drawing tooth from patient)
[presumably this is a 'ready-made', cut from a book or print]

What!?

Edwd Glase
Clock & Watch Maker Bridgnorth
Repeating Watches Carefully Repaired

W. Owen
Clock & Watch Maker
Jeweller & Silversmith
Oswestry

Bowen & Downes
Watch & Clock Makers
London

John Wieland
Clock & Watch Maker
Penton Row, Walworth
Tempus Fugit

An un-cut watch-paper of Jonathan Ager,
watch and clock-maker
Clerkenwell, London

Johnathan Woollett,
Watch & Clock Maker, Maidstone

Watchpaper; painted with grotesque seated woman with bowl of gruel

Watchpaper; printed in colour with three angels
surrounding a circular cartouche on which
is written the Lord's Prayer (about 1818)

Watch-paper in situ
(Aaaah! so that's what they do with them!!)
[random image from some auction site]
Moments in Time
1360: Henry de Vick constructs the first (totally) mechanical clock for King Charles V of France [arguable? probably]
1475: First record of a minute hand on a clock
Mid-1500s: First wearable timepieces: several inches in diameter worn on chain around the neck or pinned to the clothes --- "later in the century there was a trend for unusually shaped watches, and clock-watches shaped like books, animals, fruit, stars, flowers, insects, crosses, and even skulls (Death's head watches) were made."
1610: Glass face covers first appear
1675: King Charles II of England introduced waistcoats which coincides with the ascendancy of the pocketwatch (first made in the early 1500s) over the more cumbersome timepieces
1850: Mass production, jewel bearings, interchangeable parts; price fall leads to a great increase in the numbers of people gadding about with their own horological device
WWI: Wrist watches begin their ascendancy (checking a pocketwatch was inconvenient as a soldier)
Hands up anyone who knew what a watch-paper print was? Yeah, I thought so. Me neither. Even after jagging all the images I wasn't quite sure how they were specifically used until I found that last picture above.
Originally designed as a simple protective insert, watch-papers came to be used as an advertising medium for the watchmakers in the second half of the 18th century and another means by which print artists could ply their trade. These types of 'professional' or conservative watch-papers form the majority of the genre, but a popular 'amateur' variety also emerged that were valued as keepsakes.
"Women embroidered flower patterns on silk watch papers and made cutout or pinpricked designs of hearts, doves, forget-me-nots and wreaths. They also made them of woven hair or crocheted them from fine silk thread or quilted them. Hand-stitched monograms in wreaths of laurel or moss roses and hand-painted watch papers were especially popular.
Often early handmade watch papers took the form of a valentine or birthday greeting or a memorial for dead loved ones, showing a tombstone shadowed by a weeping willow. Examples have also been found with the Lord's Prayer in minute hand-writing and with a miniature map of part of the United States."
The British Museum Prints database has over 700 specimens of watch-paper prints available and although there is often little in the way of background, I would think the average date is around 1800
(I believe a large proportion of their stock derives from a single donor collection). [toggle down to 'object type' and search with 'watch-paper']